
In MO theory, a star (*) sign always indicates an anti-bonding orbital.įollowing the aufbau ('building up') principle, we place the two electrons in the H 2 molecule in the lowest energy molecular orbital, which is the (bonding) sigma orbital. These bonds are by far the most common in. The second, sigma-star ( σ *) orbital is higher in energy than the two atomic 1 s orbitals, and is referred to as an anti-bonding molecular orbital. KEY CONCEPT and Bonds Sigma () bonds are formed by headto-head or tail-to-tail overlap of atomic orbitals. According to MO theory, the first sigma orbital is lower in energy than either of the two isolated atomic 1 s orbitals – thus this sigma orbital is referred to as a bonding molecular orbital. And now Im saying that the energy gained from a Sigma and Pi because theres a double bond is 5 99. When two atomic 1 s orbitals combine in the formation of H 2, the result is two molecular orbitals called sigma ( σ) orbitals. The bonding in H 2, then, is due to the formation of a new molecular orbital (MO), in which a pair of electrons is delocalized around two hydrogen nuclei.Īn important principle of quantum mechanical theory is that when orbitals combine, the number of orbitals before the combination takes place must equal the number of new orbitals that result – orbitals don’t just disappear! We saw this previously when we discussed hybrid orbitals: one s and three p orbitals make four sp 3 hybrids. A sigma bond is stronger than the pi bond due to a greater and stronger overlap of orbitals. This phenomenon is due to the increase in electron density when approaching orbitals overlap. Overlapping of orbital The greater the overlapping is, the stronger the bonding will be. We have a total of one pi bond in the ethylene molecule. The stability of sigma and pi bonds depends upon the extent of.
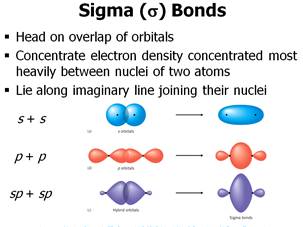
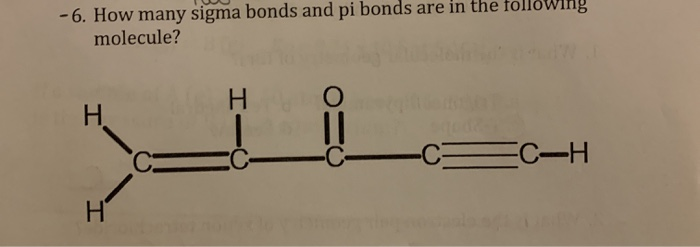
If you have a double bond, one of those bonds, the sigma bond and one of those bonds is a pi bond. These two new orbitals, instead of describing the likely location of an electron around a single nucleus, describe the location of an electron pair around two or more nuclei. When youre looking at the dot structure, one of these bonds is the pi bonds, Im just gonna say its this one right here. Thus the pi molecular orbital is higher in energy and is the highest occupied molecular orbital (the HOMO). The pi bond between the two carbon atoms has one node in the plane of the molecule. Sigma orbital is place in the axis of two nuclei: thus, a rotation of one the atoms with. Pi loturak ematen dira hibridatu gabeko p orbitalen artean. If multiple bonds happen between two atoms, the rest of bonds will be pi bonds.

In molecular orbital theory, we make a further statement: we say that the two atomic 1 s orbitals don’t just overlap, they actually combine to form two completely new orbitals. The sigma bond between the two carbon atoms does not have a node in the plane of the molecule. The first bond that forms between two atoms is a sigma bond that is, a maximum overlapping takes place. When we described the hydrogen molecule using valence bond theory, we said that the two 1 s orbitals from each atom overlap, allowing the two electrons to be shared and thus forming a covalent bond. Let’s consider again the simplest possible covalent bond: the one in molecular hydrogen (H 2). \)Īnother look at the H 2 molecule: bonding and anti-bonding sigma molecular orbitals


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
